
■ A way for the sender to correlate samples in the captured data to the capture device clock. ■ A way for the sender to read the device clock of the capture device in real time, and therefore correlate the capture device clock to NTP wall clock time. However, a better way to map the captured samples to NTP time is for the capture device to provide two features: One method of calculating this time is by observing the time of the NTP wall clock and then subtracting the predicted latency through the audio capture hardware. When the sender processes an interrupt, the sender must calculate the NTP time of the first sample in each audio packet, corresponding to the moment in time when the sample entered the microphone. Typically, the audio capture device makes a new packet of audio data available to the main processor and then triggers an interrupt to allow the processor to retrieve the packet. For instance, to determine the exact point in time when the capture device samples the audio, the sender might need to take into account delays in the capture hardware. The sender can now transmit the RTCP packet with the proper NTP and RTP time stamps.ĭetermining the values of offset and scale is nontrivial because the sender must figure out the NTP and RTP time stamps at the moment the capture sensor (microphone or camera) captures the data.

After the sender determines the NTP time stamp for the RTCP packet, the sender calculates the corresponding RTP time stamp from the preceding relationship as follows: To perform this calculation, the sender must anticipate the network interface delay.Ģ. In other words, the sender must predict the precise time at which the RTCP packet will appear on the network and then use the corresponding NTP clock time as the value that will appear inside the RTCP packet. The sender must calculate this time stamp carefully, because the time stamp must correspond to the real-time value of the NTP clock when the RTCP packet appears on the network. The sender first selects an NTP time stamp for the RTCP packet. The clocks have both an offset and a scale relationship, according to the following equation:Īfter determining this relationship by calculating the offset and scale values, the sender creates the RTCP packet in two steps:ġ.
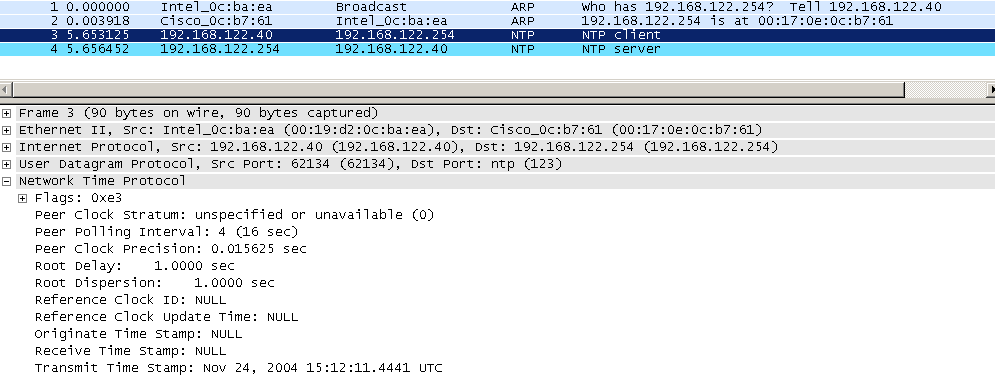
The sender calculates the relationship between its NTP timebase and the RTP media stream by observing the value of the RTP media capture clock and the NTP wall clock in real time. This pair of time stamps communicates the relationship between the NTP time and RTP time for each media stream. As a result, RTCP packets consume a small amount of bandwidth compared to the RTP media stream.įor each RTP stream, the sender issues RTCP packets at regular intervals, and those packets contain a pair of time stamps: an NTP time stamp, and the corresponding RTP time stamp associated with that RTP stream. Each RTP stream has an associated RTCP packet stream, and the sender transmits an RTCP packet once every few seconds, according to a formula given in RFC 3550.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
